In recent years, medicinal products for the EU market have been increasingly manufactured outside the EU. While this trend is particularly noticeable in the production of active ingredients, it is also becoming more prevalent in the manufacture of finished medicinal products.
At the same time, globalization has made pharmaceutical supply chains more complex. To ensure oversight, the EU classifies medicine importers as manufacturers, requiring them to obtain a Manufacturing Import Authorization (MIA) and comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations.
This framework mandates the implementation of a pharmaceutical quality system, adequate staffing and facilities, complaint and recall management, and strict supply chain control.
In this guide, we will explore the key aspects of GMP Annex 21, its implications for medicine importers, and best practices to ensure compliance.
GMP Annex 21: overview
GMP Annex 21 establishes GMP requirements for MIA holders importing medicinal products from outside the EU/EEA. The annex applies to:
- medicinal products for human use
- medicinal products for veterinary use
- investigational medicinal products
However, it does not cover products without an EU/EEA marketing authorization that are directly re-exported.
Defining 'import' under GMP Annex 21
The Annex provides a common interpretation of import, defining it as the physical introduction of a medicinal product from outside the EU/EEA.
Importation is a regulated process, and batch release by a Qualified Person (QP) can only take place after physical importation and customs clearance within an EU/EEA state.
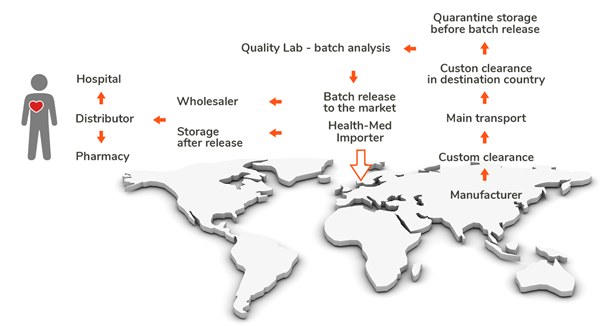
Key sites in the importation process
GMP Annex 21 highlights two critical sites involved in the importation of medicinal products:
- Site of physical import – The location where the medicinal product first enters the EU.
- Site of QP certification – Where a Qualified Person (QP) performs batch certification before release.
These sites must be considered in the broader context of the entire supply chain, which also involves:
-
API manufacturers
-
Third-country medicinal product manufacturers
-
Transport companies
-
QC testing facilities for imported products
-
Marketing Authorization Holders (MAH)

Compliance requirements for importers
For medicinal products imported from countries without a Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA), EU law mandates batch testing upon importation before QP certification and release in accordance with GMP Annex 16.
The location of testing and minimum testing requirements are outlined in:
- Article 51(1)(b) of Directive 2001/83/EC (for medicinal products for human use)
- Article 55(1)(b) of Directive 2001/82/EC (for veterinary medicines)
Reference to Eudralex guidance
GMP Annex 21 references other Eudralex chapters and annexes, particularly Annex 16, which already defines the responsibilities of a Qualified Person (QP) for batch certification and release.
However, Annex 21 further emphasizes the role of the Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) in ensuring GMP compliance throughout the importation and manufacturing process.
For example:
- The MAH must ensure that QPs have full access to batch documentation at all times.
- The MAH holds ultimate responsibility for the marketing of medicinal products and must have written agreements in place with all relevant sites.
Product Quality Review (PQR) in importation
Annex 21 also clarifies Product Quality Review (PQR) requirements for imported products. The certifying QP must:
- compare analytical results from the import test site with the certificate of analysis from the third-country manufacturer.
- Ensure an ongoing stability program is in place, even if testing occurs in a third country, as long as the QP has access to stability data.
Conclusion
As pharmaceutical manufacturing and supply chains continue to globalize, GMP Annex 21 plays a crucial role in ensuring regulatory oversight of imported medicinal products.
The annex strengthens the framework for MIA holders, emphasizing QP responsibilities, supply chain integrity, and rigorous quality control.
Companies involved in importing medicines into the EU must stay ahead of compliance requirements, ensure robust documentation, and establish strong collaborations across the supply chain.
Need support with GMP compliance for importing medicines?
At QbD Group, we provide comprehensive services for companies importing medicines into the EU. Our GMP-certified laboratory and Qualified Person (QP) services ensure seamless batch release, regulatory compliance, and efficient importation processes.
Let’s simplify your EU market access. Contact our experts today.







.png?width=109&height=108&name=Pharma%20(2).png)
.png?width=111&height=108&name=Medical%20Devices%20(2).png)
.png?width=84&height=107&name=IVD%20(2).png)




.png)