In this post, we are going to explain:
- what a CSV periodic review is,
- what its purpose is,
- and how often you should perform them.
We will also talk about the process to follow, and the minimum documentation needed to perform a risk-based periodic review of your validated systems.
What is a ‘Periodic Review’ in CSV?
A Periodic Review is an assessment of various elements to determine the validation status and the actions required to maintain the validated state of systems or equipment, through which we will demonstrate and ensure that they remain fit for their intended use.
What do we mean by ‘Maintenance of Validated Status’?
To maintain a validated state, companies must take all steps to document and analyze changes, errors, or malfunctions in a system or equipment to determine if it still fits the purpose and process it serves.
‘Maintaining validated status’ includes continuously demonstrating via review of process data, change control, deviations, corrective and preventive actions, and other related activities, that the manufacturing process remains under control and results in a product that ensures quality and patient safety.
What is the purpose of CSV Periodic Reviews?
The purpose of a periodic review is to confirm that systems are maintained in a validated state and comply with all applicable standards and procedures throughout their operational life cycle.
Frequency of CSV Periodic Reviews
Depending on the GxP impact of your system, the frequency of the periodic review should be determined. The minimum recommended frequency is once a year after the system or equipment is released for productive use.
The most common elements to consider during a CSV periodic review
The most common elements to consider during a Periodic Review are:
|
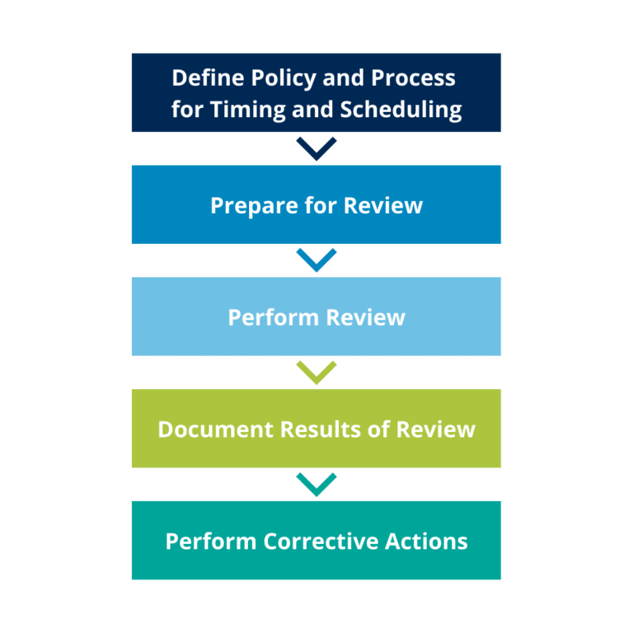
In general, the process you choose to conduct CSV Periodic Reviews should be outlined in a standard operating procedure (SOP) with templates needed to conduct the evaluation.
Considerations
Finally, it is important to keep these considerations in mind regarding CSV Periodic Reviews:
|
Need help?
Do you need help with the preparation of your SOP and templates for the Periodic Review of your systems? Or would you rather have an expert support you in the complete process of periodic reviews of all your GxP systems? QbD Group is happy to help you out!







.png?width=109&height=108&name=Pharma%20(2).png)
.png?width=111&height=108&name=Medical%20Devices%20(2).png)
.png?width=84&height=107&name=IVD%20(2).png)


.png)

.png)

.png)





.jpg)