- Scope
- Principle
- Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS)
- Premises
- Equipment
- Utilities
- Personnel
- Production and specific technologies
- Environmental and process monitoring
- Quality control (QC)
- Glossary
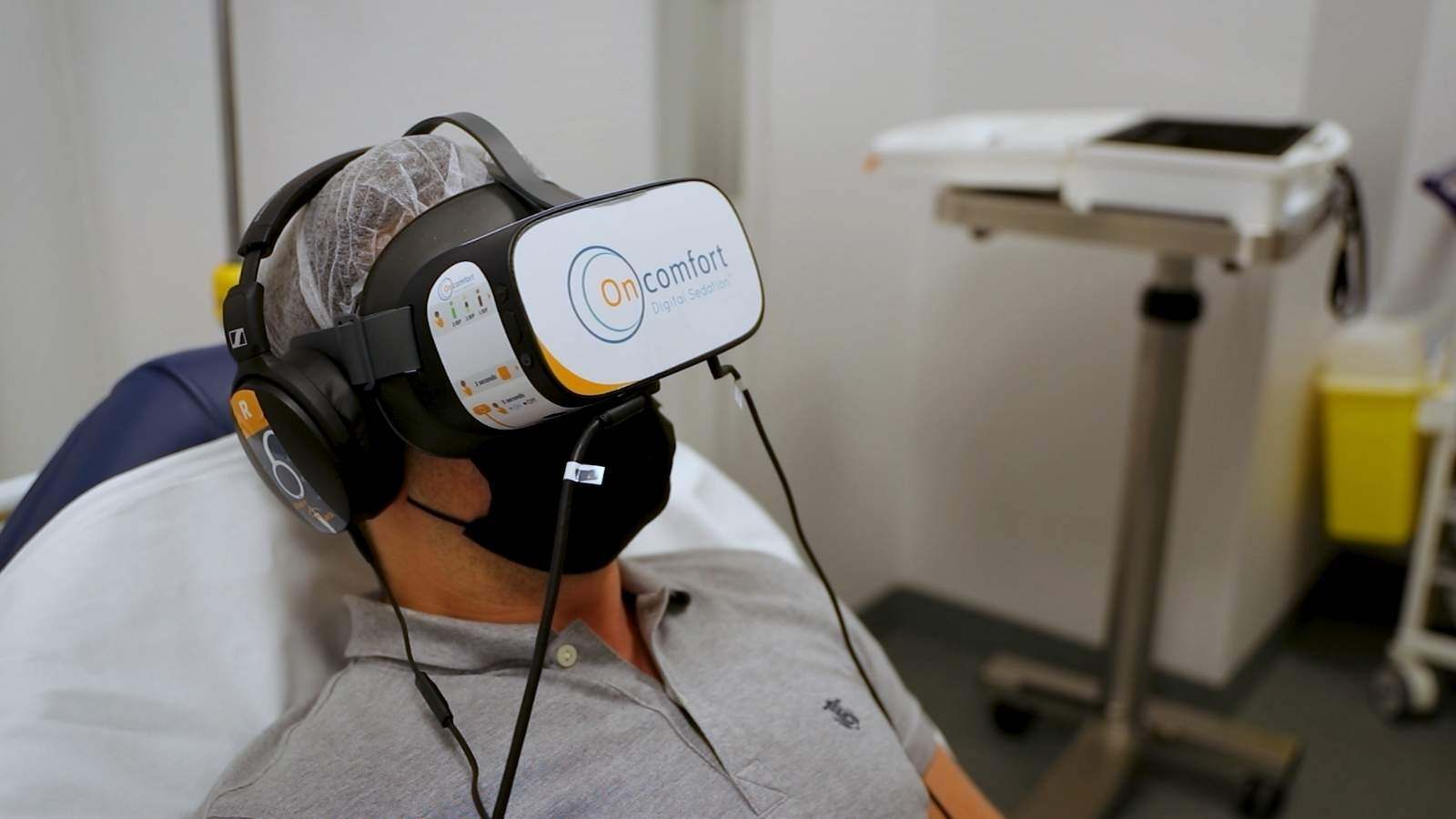
In this blog post, we will provide a summary of the changes and our initial insights several months after the revision.
EU GMP Annex 1’s Revision: overview and insights
Scope, Principle, and Glossary
The scope of the EU GMP Annex 1 has been expanded to include additional areas beyond sterile products, such as:
-
contamination control strategy,
-
design of premises,
-
cleanroom classification,
-
qualification,
-
validation,
-
monitoring,
-
and personnel gowning.
The revised “Scope” and “Principle” sections now clearly reference the importance of applying the principles of Quality Risk Management (QRM).
In addition, key areas and special requirements for sterile products are now more clearly listed and divided into 3 categories. Laslty, a glossary has been added to provide guidance on specific terminology, avoiding ambiguity and inconsistencies.
Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS)
A new concept brought into EU GMP Annex 1 is the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) for sterile product manufacture. This section – related to ICH Q10 Quality Management System – lists the specific requirements for sterile product manufacture and takes generic approaches into scope:
-
risk management,
-
sufficient knowledge and process understanding,
-
proper non-conformity and CAPA management,
-
MGMT responsibility,
-
access to information for certain responsibilities,
-
…
The importance of non-conformity investigation related to sterility or microbiological load is emphasized.
Premises
The revised “Premises” chapter now clearly uses the term “cleanrooms” and outlines the different classes and requirements for classification.
The importance of both “at rest” and “operational” is emphasized, and requirements for total particle concentration and allowable microbial contamination have been slightly changed.
Specific reference is made to the need for periodic re-qualification of cleanrooms and clean air equipment. The use of Restricted Access Barrier Systems (RABS) in addition to isolators as a barrier technology is introduced.
This section also contains a comprehensive description of the design and use of airlocks, along with clear specifications for airflow patterns and air pressure requirements.
Finally, a new requirement is added, namely the need to be able to observe Class A and B areas from the outside.
Equipment
The revised “Equipment” chapter outlines the need for an equipment design description, and precautions related to equipment design and installation are outlined in more detail. Finally, the need for a cleaning and sterilization process (if applicable) of the equipment has been added.
First insights into the impact of EU GMP Annex 1’s revision
After a few months of these new guidelines, the full extent of the impact is not yet fully understood. Many of the updates and clarifications added in this new version were already in practice in some organizations.
Smaller organizations may need to make some extra effort to bring their level of compliance up to the new standard. One of the bigger challenges is the Contamination Control Strategy, which requires a multidisciplinary approach. There are also challenges for QA – the approving party – as it is a new concept and it is not always clear what the minimum requirements are to meet this update.
Disclaimer: To be successful in inspections by competent authorities or third parties, it is important to do a full gap assessment. This will show if the update is fully compliant or if there are certain gaps.








.jpg)






.png)

.jpg)